How do protons identify an atom?
1 Answer
The number of protons gives

Explanation:
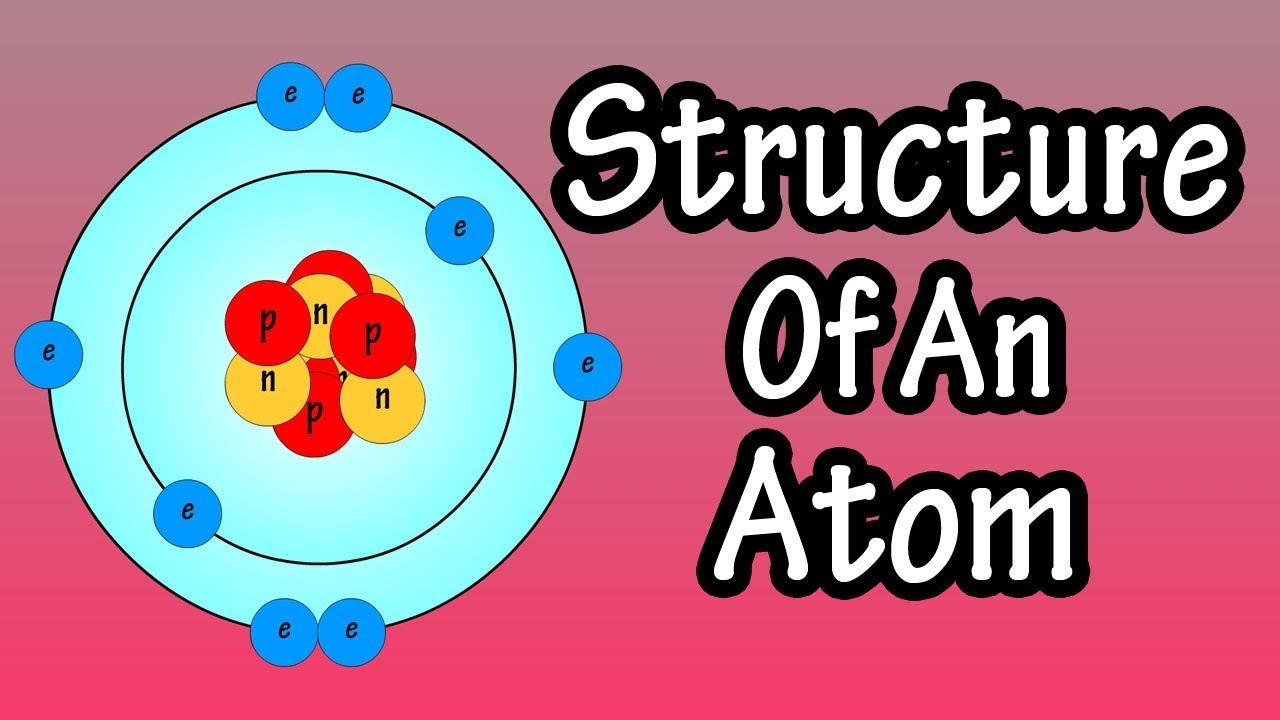
Protons make up part of the nucleus of all atoms except hydrogen, whose nucleus consists of a single proton. In neutral atoms, the number of protons is the same as the number of electrons. In positively charged atoms, the number of protons is greater than the number of electrons, and in negatively charged atoms electrons outnumber protons. Proton: 1 n a stable particle with positive charge equal to the negative charge of an electron Types: hydrogen ion a positively charged atom of hydrogen; that is to say, a normal hydrogen atomic nucleus Type of: nucleon a constituent (proton or neutron) of an atomic nucleus.
Atom song for kids explains the three parts of an atom-protons, neutrons and electrons-as well as what a nucleus. Protons make the nucleus, or center, of an atom. The simplest atoms – hydrogen atoms – have a nucleus made of just one proton. Apple mac theme for windows 7 free download. But most atoms have more than one proton, and at least one neutron to go with each proton (some have more than one). Protons are actually made of even smaller invisible particles, called quarks. Each proton has three quarks, two up quarks and one down quark.
Proton Atom Symbol

In the neutral atom, the value of
Skype for business mac client download. In the nucleus itself, there may be as many protons or less AS neutrons, massive particles of zero electronic charge. Interactions between nuclear protons and neutrons, at unfeasibly short nuclear ranges, give rise to the strong nuclear force, the which, at this short range, is strong enough to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between the positively charged protons.
I have written here before that the choice of a negatively charged electronic charge, and a positively charged nuclear charge is a bit unfortunate in that chemists who deal with many electron atoms often get the right magnitude but the wrong charge in their calculations, simply because they counted odd instead of even or even instead of odd. The much smaller company of particle physicists, who are a bit on the weird side anyway, could have coped with a nuclear particle that had a negative electronic charge. Alas we are stuck with the convention.
Related questions
An example of a proton is the single proton in the nucleus of a hydrogen atom.
Proton Atom Charge

Proton Atomic Number
Origin of proton
- From Greek prōtonneuter ofprōtosfirstper1 in Indo-European roots
From American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, 5th Edition
- From Ancient Greek Ï€Ïῶτον (prÅton), neuter of Ï€Ïῶτος (prÅtos, “first')
From Wiktionary
